Nexus NFT Platform
This comprehensive example demonstrates how to build a production-ready NFT platform on the Nexus blockchain: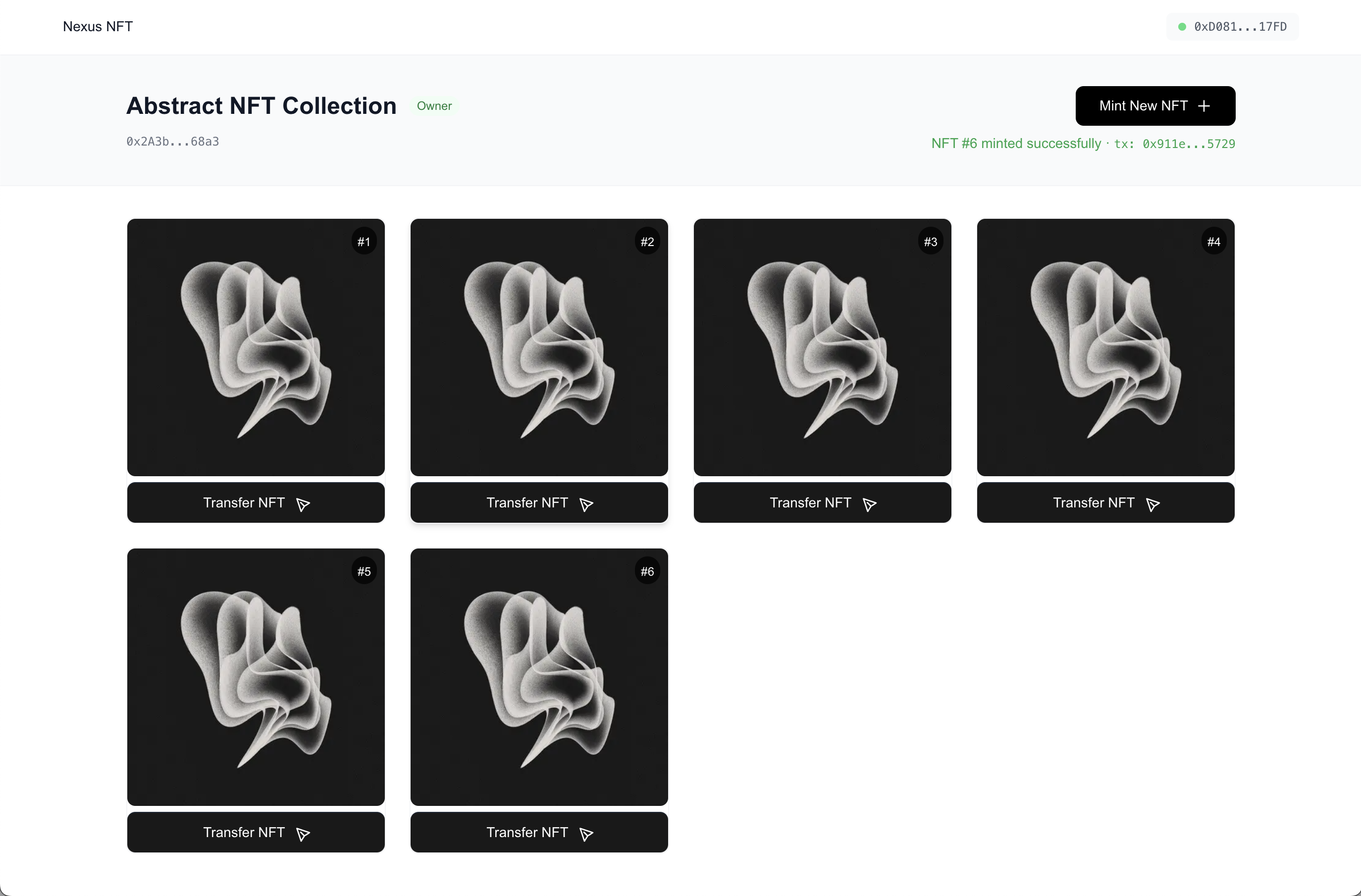
- Live Demo: https://nexus-nft-example.vercel.app/
- GitHub: https://github.com/nexus-xyz/nexus-nft-example
Overview
This project showcases a modern, full-stack NFT platform built with Next.js 13+ (App Router), TypeScript, Hardhat, and ethers.js v6. It demonstrates:- ERC-721 compliant NFT smart contract with metadata management
- Next.js frontend with App Router architecture
- Firebase Storage integration for NFT image hosting
- OpenSea-compatible metadata API
- Wallet integration with MetaMask
- Vercel deployment pipeline
- Create and deploy custom NFT collections
- Upload and manage collection artwork
- Mint NFTs to any address
- View and transfer owned NFTs
- Update collection metadata (when not frozen)
What is this project?
The core file in our project (SimpleNFT.sol) is a smart contract written in the Solidity programming language. Smart contracts are programs that run on blockchains like Ethereum. They can hold assets, enforce rules, and let people interact with them in a trustless way.
What is an NFT?
NFT stands for Non-Fungible Token:- Token: A digital asset on a blockchain.
- Non-Fungible: Each token is unique and not interchangeable with another (unlike, say, dollars or Bitcoin).
What does this contract do?
This contract lets you create and manage NFTs. Here’s what it provides, step by step:- Creating NFTs (Minting):
- The contract can create new NFTs and assign them to people’s addresses (like digital wallets).
- Each NFT has a unique number (called a token ID).
- Metadata:
- Each NFT can have associated information (like a link to an image, or a description). This is called metadata.
- The contract lets the owner set a “base URI” (a web address that points to the metadata for all NFTs).
- Ownership:
- The contract has an “owner” (usually the person who deployed it).
- Only the owner can change certain things, like the base URI or “freeze” the metadata.
- Freezing Metadata:
- Once the owner is happy with the metadata, they can “freeze” it. After that, it can’t be changed—this is important for collectors who want to know their NFT won’t change in the future.
- Batch Minting:
- The contract can create (“mint”) multiple NFTs at once, which is useful for projects that want to launch a collection.
How does it work?
- People interact with the contract by calling its functions (like
mintto create an NFT). - The contract keeps track of who owns which NFT.
- The contract follows a standard (ERC-721) so that wallets, marketplaces, and other tools know how to work with it.
Why use this contract?
If you want to create a collection of unique digital items (NFTs) on a blockchain, this contract gives you the basic tools to do that securely and in a way that’s compatible with the wider NFT ecosystem.Setting Up Your Development Environment
1. Install Required Tools
2. Create a New Project
3. Configure Hardhat for Nexus
Within your project directory, create/update your config filehardhat.config.js which will define the network configuration, RPC endpoint for Hardhat to connect to, and chainID for signature verification:
4. Configure your private key in .env file
-
Get your private key from Nexus
- Go to the Nexus Web App
- Sign in to your account in the top right corner
- Click the “Settings” tab
- Navigate to “Account & Security”
- Click on “Private Key”
- Click “Reveal” to view your private key
-
Create your .env file
- Create a new file named
.envin your project root directory - Add your private key in this format:
- Create a new file named
-
Install dotenv package
-
Update hardhat.config.js
- Add this line at the top of your
hardhat.config.jsif not already present:
- Add this line at the top of your
- Never share your private key
- Never commit it to version control
- Keep it secure and backed up
- Use a test account for development
5. Receive test NEX from a faucet for contract deployment
To deploy your contract on Nexus Layer 1, you’ll need NEX tokens to pay for gas fees. Gas fees are the cost of executing transactions on the blockchain, similar to how you need fuel to drive a car. There are two ways to receive NEX for testing:-
Earn NEX through Proving
- Submit proofs to earn points and NEX in real-time
- This is the recommended way as it helps secure the network
- For detailed instructions on proving, visit our Proving Guide
-
Use the Nexus Faucet
- A faucet is a service that provides small amounts of cryptocurrency for testing.
- It’s like a water faucet, but instead of water, it dispenses test tokens
- Visit our Faucet to receive test NEX
Smart Contract Architecture
1. Create a Contract File
Createcontracts/SimpleNFT.sol. The project uses an advanced ERC-721 implementation with enhanced metadata management, tailored for NFT collections requiring scalable minting, secure update mechanisms, and compatibility with modern NFT marketplaces.
SimpleNFT, extends the ERC-721 standard to support modern NFT use cases including batch minting, dynamic metadata with optional freezing, and ERC-4906 metadata update events. It is built atop OpenZeppelin libraries for security and standard compliance.
Key Features
ERC-721 Compliance Inherits from OpenZeppelin’sERC721 and ERC721URIStorage, enabling both standard NFT transfer and ownership logic and per-token URI storage.
Batch Minting
Allows efficient minting of multiple NFTs in a single transaction. Useful for creators distributing large collections or performing airdrops.
Metadata Control and Freezing
The base URI can be updated by the owner until freezeMetadata() is called. Once frozen, metadata becomes immutable, which is critical for collectors and marketplaces relying on permanent content.
ERC-4906 Support
Implements the ERC-4906 interface, which allows external platforms to detect when metadata has changed. The setBaseURI method emits a BatchMetadataUpdate event covering all tokens.
Ownership and Access Control
Relies on OpenZeppelin’s Ownable pattern to restrict administrative functions (setBaseURI, freezeMetadata) to the contract owner.
Gas Efficiency
Uses a simple incrementing counter (_nextTokenId) to assign token IDs, reducing storage complexity and minimizing gas costs. Batch minting via loops avoids external calls, maintaining compact logic.
Function Breakdown
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
constructor(...) | Initializes contract with name, symbol, and base URI; sets ownership |
_baseURI() | Internal getter for the stored baseURI |
setBaseURI(...) | Allows the owner to update metadata base URI; emits ERC-4906 update signal |
freezeMetadata() | Permanently disables URI updates and emits a MetadataFrozen event |
safeMint(...) | Mints a single token to the specified address |
batchMint(...) | Mints multiple tokens to a single address and returns all token IDs |
tokenURI(...) | Resolves the final token URI using base URI or stored value |
supportsInterface(...) | Advertises interface support for ERC-721, metadata extension, and ERC-4906 |
2. Create a Deployment Script
Createscripts/deploy.js:
A deployment script is a programmatic way to deploy your smart contracts to a blockchain using Hardhat. Instead of manually interacting with the network through a UI or console, deployment scripts allow you to:
- Automate contract deployment
- Set constructor arguments dynamically
- Log or save deployed addresses
- Chain deployments in a predictable order
- Integrate easily into testing, development, or CI/CD pipelines
- It manages asynchronous deployment logic with await
- Provides helpful logs to track progress
- Prepares for contract verification on Nexus Explorer
Deploying Your Contract
1. Deploy to Nexus
Run the following command to deploy your contract to the Nexus network:2. Examine Counter contract on the Nexus Explorer
Visit the Testnet III Nexus Explorer to view your deployed contract. The block explorer is a search engine for the blockchain that lets you:- View all transactions
- Check contract code
- Monitor contract interactions
- Track token transfers
- View account balances
- Copy your contract’s address from the deployment output
- Paste it into the search bar at the top of the explorer
- Click on your contract to view its details
- Contract code (verified)
- Transaction history
- Contract balance
- Recent interactions
- Event logs
Project Structure
The project follows a modern full-stack architecture:Setting Up Firebase Storage
The platform uses Firebase Storage for hosting NFT images. Here’s how to set it up:1. Create a Firebase Project
- Go to the Firebase Console
- Click “Add project” and follow the setup wizard
- Enable Firebase Storage in your project
2. Configure Security Rules
Set up proper security rules for your Firebase Storage:3. Add Firebase Configuration
Create a.env.local file in the frontend directory:
4. Initialize Firebase in Your Application
OpenSea-Compatible Metadata API
The platform includes an API that generates OpenSea-compatible metadata:- Proper naming and description
- Image URL (either from Firebase or a generated SVG)
- External URL for viewing the NFT
- Attributes as traits
Frontend Integration with ethers.js v6
The frontend uses ethers.js v6 to interact with the smart contract:Deploying to Vercel
The project is optimized for deployment on Vercel:1. Connect Your GitHub Repository
- Push your project to GitHub
- Log in to Vercel
- Click “New Project” and select your repository
2. Configure Environment Variables
Add all required environment variables in the Vercel project settings:- Firebase configuration
- API URLs
- Contract addresses (if pre-deployed)
3. Configure Build Settings
Set the following build configuration:- Framework Preset: Next.js
- Root Directory:
frontend - Build Command:
npm run build - Output Directory:
.next
4. Deploy
Click “Deploy” and Vercel will automatically build and deploy your application.5. Set Up Custom Domain (Optional)
For a professional look, configure a custom domain in the Vercel project settings.Extending the Platform
This template can be extended in several ways:1. Advanced Marketplace Features
Add buying, selling, and auction functionality:- Implement ERC-2981 for royalties
- Create listing and offer contracts
- Build a marketplace interface
2. Enhanced Metadata and Rendering
Improve the NFT display and metadata:- Add on-chain metadata storage options
- Implement 3D model support
- Create interactive NFTs with HTML rendering
3. Multi-chain Support
Extend to support multiple blockchains:- Add network switching logic
- Implement cross-chain bridging
- Create unified collection management
4. Social Features
Add community elements:- NFT comments and reactions
- Collection following
- Creator profiles and verification
5. Analytics Dashboard
Build analytics for creators:- Minting and transfer statistics
- Holder demographics
- Secondary market performance
Security Considerations
When deploying your own version, consider these security aspects:-
Smart Contract Security:
- Use OpenZeppelin contracts for standard implementations
- Implement access control for administrative functions
- Consider a contract audit for production deployments
- Test thoroughly on testnet before mainnet deployment
-
Frontend Security:
- Protect API keys with environment variables
- Implement proper authentication for admin functions
- Validate all user inputs
- Use HTTPS for all connections
-
Firebase Security:
- Configure strict security rules
- Limit file sizes and types
- Set up proper authentication
- Enable Firebase Security features
Resources
- Web URL: https://nexus-nft-example.vercel.app/
- GitHub: https://github.com/nexus-xyz/nexus-nft-example
- Clone the repository and install dependencies:
- Deploy the contracts:
-
Update the deplyed contract address in the
frontend/src/app/page.tsxfile. - Start the frontend:

